Actions, IWorkflowActionProvider and CodeActions
To put it simply, Action is a method called when a process is being executed. Action allows you to call any code, business logic methods which your application already has, external services, side libraries methods, send mail, etc. Though extremely simple, Actions are a powerful tool of integration into an existing application.
There are two ways of creating Actions in your application: inherit the IWorkflowActionProvider interface and create Actions in this class, or create Actions right in the scheme in the CodeActions section. These two approaches may be combined.
Creation of Action in the scheme
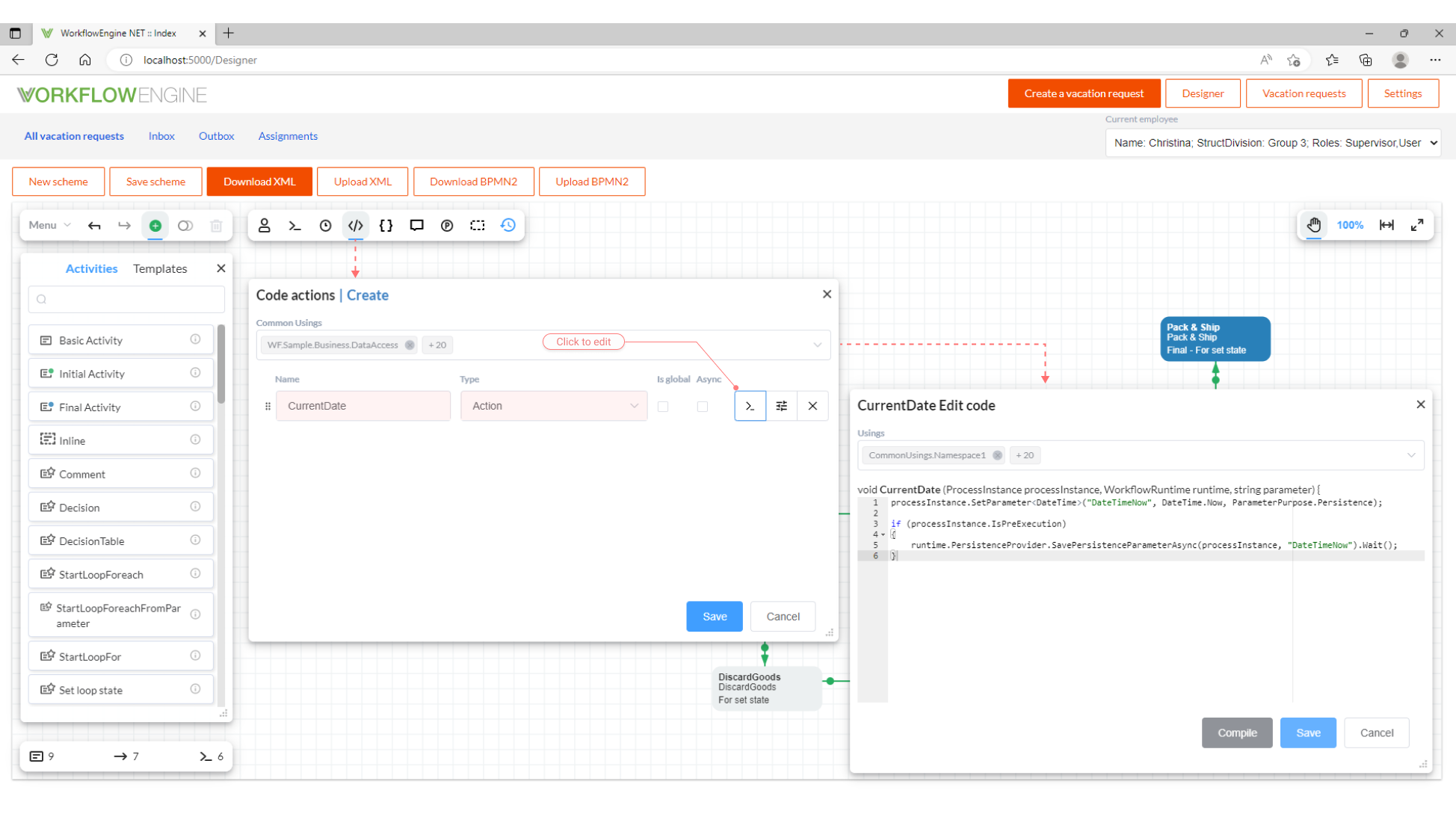
It is quite easy to create Actions (or Conditions) in Designer. Open the CodeActions window by clicking a respective button in the toolbar.
Then, create a new line, and specify the name and type - Action or Condition. Open the code editor by clicking Edit Code. Here you can write
your code in C#; use the Compile button to check whether the code is compiled correctly. You may also edit the list of included namespaces
in the Usings field. Usually, CodeActions are stored right in the scheme, and compiled once upon its first loading. However, if
attribute IsGlobal is set, CodeAction will be saved in the WorkflowGlobalParameter table (or object), and it will be possible to
utilize it in all schemes. Such CodeActions are compiled immediately upon executing of WorkflowRuntime. A simple CodeAction for retrieving
the current date-time of execution in a process Activity can be as follows:
void CurrentDate(ProcessInstance processInstance, WorkflowRuntime runtime,
string parameter) {
processInstance.SetParameter<DateTime>("DateTimeNow", DateTime.Now,
ParameterPurpose.Persistence);
// parameters are not saved in Pre-Execution mode, but if you intentionally
// want to save a parameter in Pre-Execution mode, then use the following code
if (processInstance.IsPreExecution)
{
runtime.PersistenceProvider.SavePersistenceParameterAsync(processInstance,
"DateTimeNow").Wait();
}
}
If you want to create an asynchronous Action (or Condition) in the scheme, simply tick the checkbox Async beside its name in the
CodeActions window in designer. Afterwards, you will be able to use the await keyword in the code. No further actions need to be
undertaken in this case.
In order to enable the creation of Actions in designer, you should configure WorkflowRuntime in the following way (the configuration
example already has this line):
runtime.EnableCodeActions();
If you are going to utilize methods from your assemblies in your code, you should notify WorkflowRuntime about them upon configuration:
runtime.RegisterAssemblyForCodeActions(Assembly.GetAssembly(typeof(SomeTypeFromMyAssembly)));
Besides, it is possible to set breakpoints in CodeActions for debugging purposes. To do this, you should first enable debugging upon
initialization of WorkflowRuntime:
runtime.CodeActionsDebugOn();
Then, you can set a breakpoint right in the code of CodeAction by writing /*break*/ (commentary brackets do matter). It is rather convenient because if debugging is disabled, a breakpoint will transform into an ordinary comment. At the same time, if debugging is enabled, a breakpoint will turn into the following code:
if (System.Diagnostics.Debugger.IsAttached) {
System.Diagnostics.Debugger.Break();
}
Please be aware that the code inside Code Actions is compiled dynamically and has full access to the environment in which the Workflow Engine is running. This means that allowing end users to create Code Actions can be dangerous, as it may lead to the execution of malicious code on the server. If you wish to provide such capabilities to end users, ensure that the Workflow Engine is running in an isolated environment. The safest option is to prohibit the creation of Code Actions and provide a set of pre-built Actions through a provider, as further described below.
IWorkflowActionProvider
Let's start with a code example, which you may copy and paste for a faster kick-off.
using OptimaJet.Workflow.Core.Model;
using OptimaJet.Workflow.Core.Runtime;
public class ActionProvider : IWorkflowActionProvider
{
private readonly Dictionary<string, Action<ProcessInstance, WorkflowRuntime, string>> _actions = new();
private readonly Dictionary<string, Func<ProcessInstance, WorkflowRuntime, string, CancellationToken, Task>>
_asyncActions = new();
private readonly Dictionary<string, Func<ProcessInstance, WorkflowRuntime, string, bool>> _conditions = new();
private readonly Dictionary<string, Func<ProcessInstance, WorkflowRuntime, string, CancellationToken, Task<bool>>>
_asyncConditions = new();
public ActionProvider()
{
// Register your actions in _actions and _asyncActions dictionaries
_actions.Add("MyAction", MyAction); // sync
_asyncActions.Add("MyActionAsync", MyActionAsync); // async
// Register your conditions in _conditions and _asyncConditions dictionaries
_conditions.Add("MyCondition", MyCondition); // sync
_asyncConditions.Add("MyConditionAsync", MyConditionAsync); // async
}
private void MyAction(ProcessInstance processInstance, WorkflowRuntime runtime,
string actionParameter)
{
// Execute your synchronous code here
}
private async Task MyActionAsync(ProcessInstance processInstance, WorkflowRuntime runtime,
string actionParameter, CancellationToken token)
{
// Execute your asynchronous code here. You can use await in your code.
}
private bool MyCondition(ProcessInstance processInstance, WorkflowRuntime runtime, string actionParameter)
{
// Execute your code here
return false;
}
private async Task<bool> MyConditionAsync(ProcessInstance processInstance, WorkflowRuntime runtime,
string actionParameter, CancellationToken token)
{
// Execute your asynchronous code here. You can use await in your code.
return false;
}
#region Implementation of IWorkflowActionProvider
public void ExecuteAction(string name, ProcessInstance processInstance, WorkflowRuntime runtime,
string actionParameter)
{
if (!_actions.ContainsKey(name))
{
throw new NotImplementedException($"Action with name {name} isn't implemented");
}
_actions[name].Invoke(processInstance, runtime, actionParameter);
}
public async Task ExecuteActionAsync(string name, ProcessInstance processInstance, WorkflowRuntime runtime,
string actionParameter, CancellationToken token)
{
//token.ThrowIfCancellationRequested(); // You can use the transferred token at your discretion
if (!_asyncActions.ContainsKey(name))
{
throw new NotImplementedException($"Async Action with name {name} isn't implemented");
}
await _asyncActions[name].Invoke(processInstance, runtime, actionParameter, token);
}
public bool ExecuteCondition(string name, ProcessInstance processInstance, WorkflowRuntime runtime,
string actionParameter)
{
if (_conditions.ContainsKey(name))
{
return _conditions[name].Invoke(processInstance, runtime, actionParameter);
}
throw new NotImplementedException($"Condition with name {name} isn't implemented");
}
public async Task<bool> ExecuteConditionAsync(string name, ProcessInstance processInstance,
WorkflowRuntime runtime, string actionParameter, CancellationToken token)
{
//token.ThrowIfCancellationRequested(); // You can use the transferred token at your discretion
if (_asyncConditions.ContainsKey(name))
{
return await _asyncConditions[name].Invoke(processInstance, runtime, actionParameter, token);
}
throw new NotImplementedException($"Async Condition with name {name} isn't implemented");
}
public bool IsActionAsync(string name, string schemeCode)
{
return _asyncActions.ContainsKey(name);
}
public bool IsConditionAsync(string name, string schemeCode)
{
return _asyncActions.ContainsKey(name);
}
public List<string> GetActions(string schemeCode, NamesSearchType namesSearchType)
{
return _actions.Keys.Union(_asyncActions.Keys).ToList();
}
public List<string> GetConditions(string schemeCode, NamesSearchType namesSearchType)
{
return _conditions.Keys.Union(_asyncConditions.Keys).ToList();
}
#endregion
}
Let's see how it works. Workflow Engine identifies Actions and Conditions by unique names. In order to specify Actions in the Implementation
section of an Activity, their names should be returned by the GetActions method. The same is true for Conditions in Transitions; the only
difference is that you have to use the GetConditions method. When WorkflowRuntime calls an Action, it calls the ExecuteAction method and
conveys the name of the Action to it from the scheme. Process object ProcessInstance, a link to WorkflowRuntime that called this Action,
and Action Parameter from the scheme are also conveyed to this method. Then, you need to call your code in this method. This is also true
for Conditions; the only difference is that the ExecuteCondition method with the Condition's name from the scheme is called; the called
method should return true or false.
If you need to call asynchronous methods from Actions (and Conditions) you should add their handlers _asyncActions and _asyncConditions
dictionaries, rather than _actions and _conditions. In this case the IsActionAsync and IsConditionAsync methods will return true and
the engine will call the ExecuteActionAsync and ExecuteConditionAsync methods. You can use the keyword await in these methods and call
asynchronous methods. If you are using asynchronous Actions, then you should use asynchronous versions of methods of the WorkflowRuntime
object so that your application enjoys better performance and higher efficiency. For example, use ExecuteCommandAsync instead
of ExecuteCommand and SetStateAsync instead of SetState. Pay attention to the fact, that when calling
WorkflowInit.Runtime.ExecuteCommandAsync you can pass a CancellationToken object to it. Cancellation token will be passed to
the ExecuteActionAsync and ExecuteConditionAsync methods without changes and its handling is solely up to you. You can use the token to
cancel long-running operations or to set up timeouts.
In the above-mentioned example, the IWorkflowActionProvider implementation code won't change upon adding new Actions or Conditions, and
this is good. The class contains four dictionaries that use the name of the Action (or Condition) as a key, and a delegate containing a link
to your methods as a value. That's why upon adding a new Action (or Condition), you simply need to register this method in the dictionary
under the name you would like to see in Designer. This code does not contain reflection or any other components that may slow things down.
Afterward, the provider's instance should be conveyed to WorkflowRuntime upon configuring in order to allow WorkflowRuntime learning
about the provider you created.
runtime.WithActionProvider(new ActionProvider());
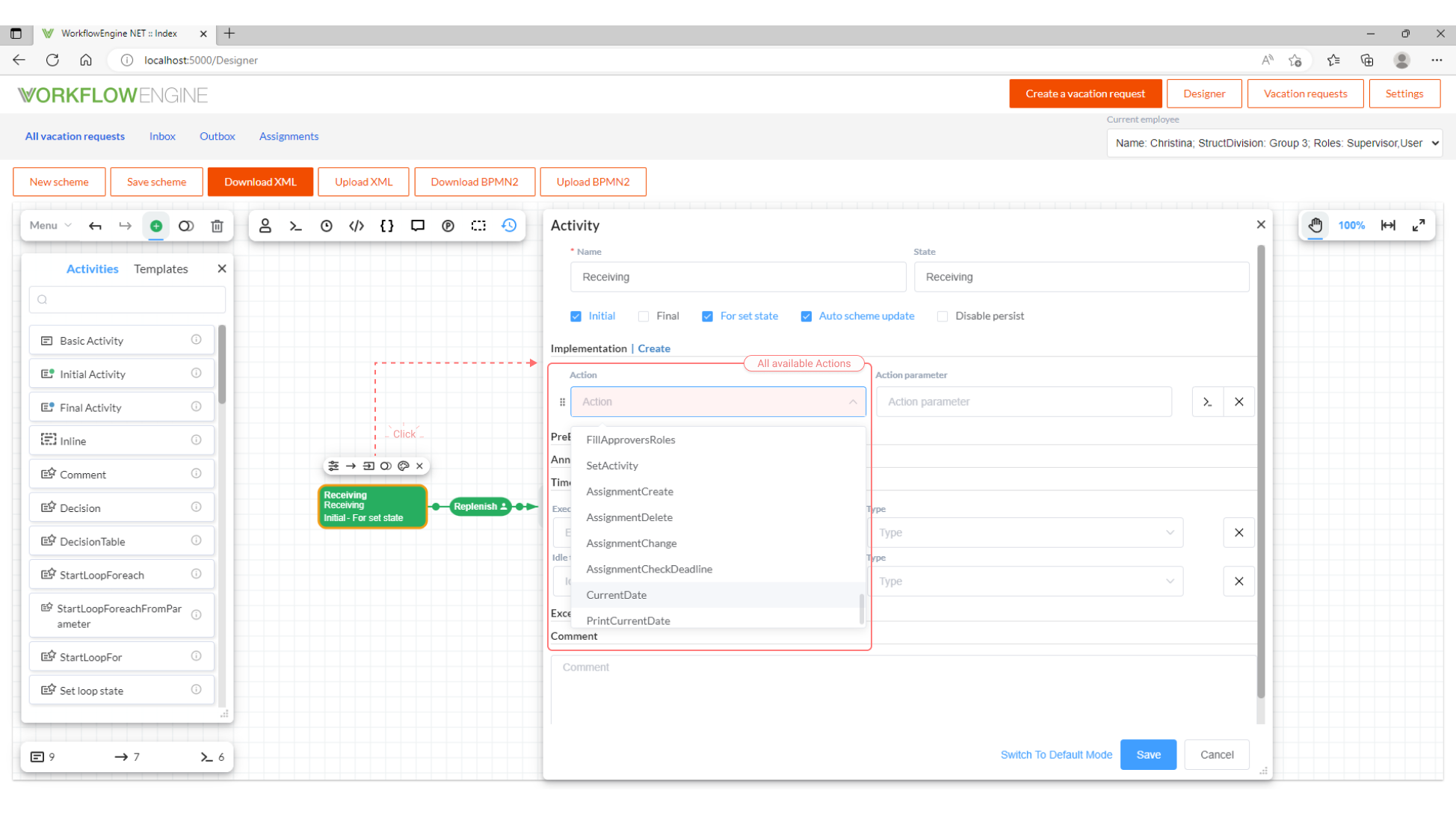
Once the new CodeAction is registered by IWorkflowActionProvider, it will be available to be used through the GUI interface in any
Activity in the Implementation section, in both normal and pre-execution mode, just by clicking the list box 'Action', and then
searching the CodeAction unique name that was set.
A combined approach
You may combine Actions created in IWorkflowProvider with those created in Designer. For example, you may set complex conditions in IWorkflowProvider, and then call and combine them in CodeActions. To do this, you should be able to call Actions from other Actions.
If you have a link to WorkflowRuntime, you can always get access to IWorkflowActionProvider:
var actionProvider = runtime.ActionProvider;
In order to call Actions created in the scheme, use the following method:
string parameter = string.Empty;
processInstance.ExecuteCodeAction("Action name", runtime, parameter);
In order to call Conditions created in the scheme, use the following method:
string parameter = string.Empty;
bool result = processInstance.ExecuteConditionFromCodeActions("Condition name", runtime, parameter);
Connection with the workflow designer
The list of Actions that you see in the workflow designer (in the Implementation section in an Activity) is formed as a combination of
string lists returned by the IWorkflowActionProvider.GetActions method and received directly from the scheme. Elements with type Action
are selected from the CodeActions section.
The list of Conditions (Actions that return a bool) that you see in the workflow designer (in the Condition section in a Transition) is
formed as a combination of string lists returned by the IWorkflowActionProvider.GetConditions method and received directly from the
scheme. Elements with type Condition are selected from the CodeActions section.
Priority of search for Action or Condition for execution
Situations where Action (or Condition) with the same name is simultaneously present in Global CodeActions, scheme CodeActions and
in IWorkflowActionProvider occur rarely. However, sometimes a need may arise to make an override and replace the Global CodeAction of a
scheme with a CodeAction from a scheme (or from IWorkflowActionProvider). The behaviour of WorkflowRuntime in this case is set with
the ExecutionSearchOrder parameter. This parameter sets the Action search priority. By default, the following search algorithm is
executed. Action (or Condition) with the specified name is searched for in CodeActions of the scheme, and, if found, it will be executed. If
it is not found, then the search in Global CodeActions is performed. If it is not found there, then the search in IWorkflowActionProvider
is performed. If it is not found in any of the three sources, then the NotImplementedException is thrown. Such a behaviour corresponds to
the following setting:
runtime.SetExecutionSearchOrder(ExecutionSearchOrder.LocalGlobalProvider);
This is a default behaviour, and you should not specify it explicitly. You can change it by specifying one of the 6 possible priorities
(LocalGlobalProvider, GlobalLocalProvider, LocalProviderGlobal, GlobalProviderLocal, ProviderLocalGlobal or ProviderGlobalLocal) which are
set in the ExecutionSearchOrder enum.
runtime.SetExecutionSearchOrder(ExecutionSearchOrder order);
Memory usage
Compiling scripts in C# requires a lot of memory. The first time a process is created, the C# scripts are compiled, resulting in a momentary
high memory spike. Memory consumption is scheme dependent. To reduce the effects of a memory spike use the WithExpressionsCompilerOptions
method to configure ExpressionsCompiler to force the garbage collector to be invoked after each script compilation and disable parallel
compilation.
runtime.WithExpressionsCompilerOptions(ExpressionsCompilerOptions.Forced)